AdjustEBOVGP-Dx
Project Coordinator: Dr Misaki Wayengera, Makerere University, Uganda
Other Beneficiaries:
- National Institute for Communicable Diseases-NICD, South Africa
- Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences-SLU, Sweden
- University of Warsaw, Poland
- Agricultural University of Athens, Greece
- GeneCUST S.A.S, France
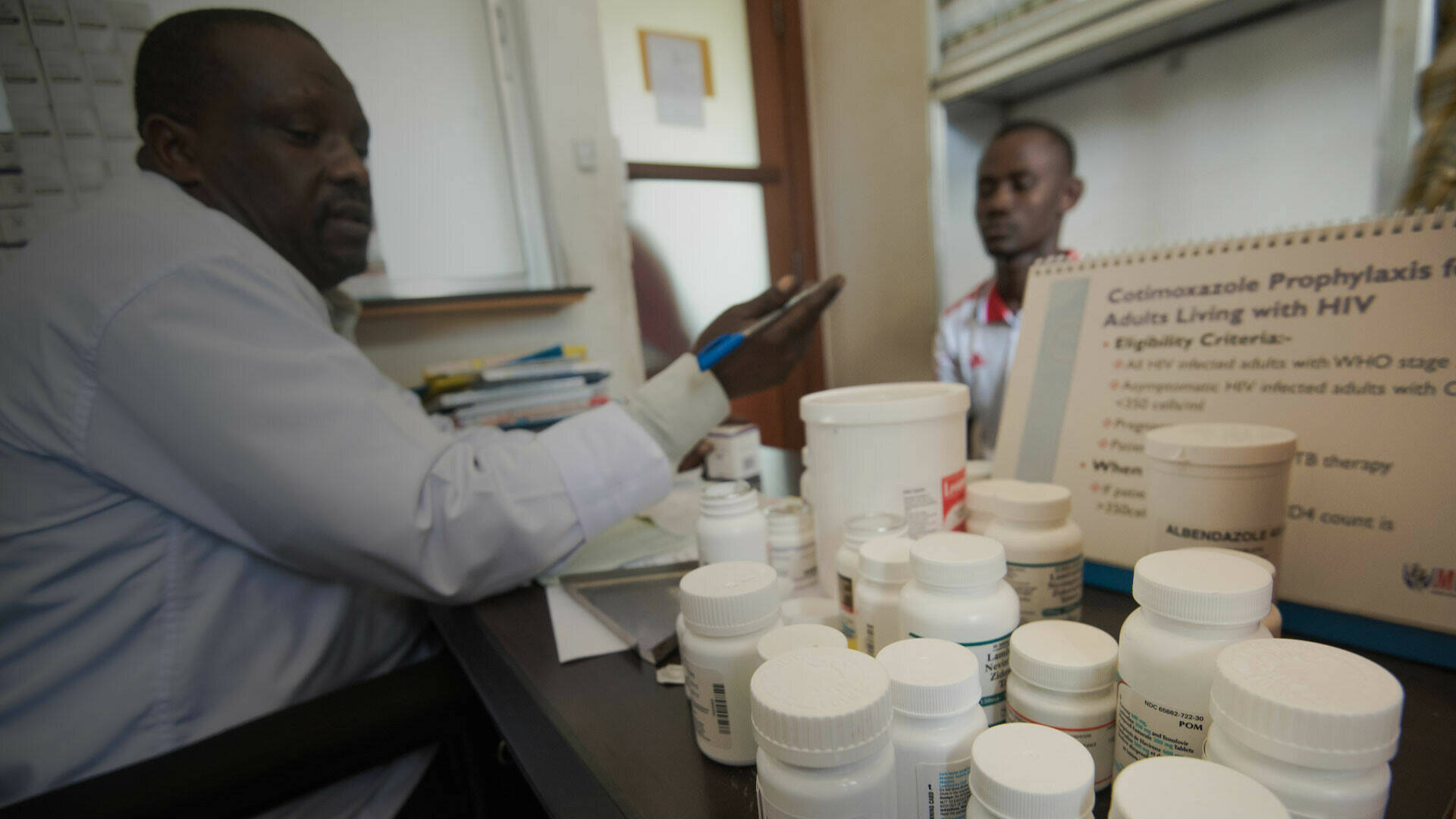
The AdjustEBOVGP-Dx project has been developing and testing a rapid point-of-care diagnostic to detect Ebola virus and to distinguish Ebola from a close relative, Marburg virus. The prototype was initially going to be tested in the Ebola outbreak region in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. However, as the outbreak was brought under control relatively quickly, the testing was carried out in South Africa using cultured virus from samples collected in Sierra Leone during the 2014-2015 outbreak. The consortium has engaged relevant authorities in local and international response to EVD in the region (INBR-DRC, MoH Uganda, FIND, WHO, etc.), and the team has established an ecosystem of GMP certified reagent suppliers and accredited RDT manufacturers (Astel Diagnostics ‘U' LTD & LifeAssays Incorp., SA) to rapidly scale up production and deployment of the RDTs. If proven clinically effective, it would be the first diagnostic able to identify infections with both Ebola and Marburg virus, another lethal viral infection with epidemic potential. As more outbreak occur, field validation of this diagnostic strategy continues, building on knowledge generated from the Emergency project.
scroll down

scroll down
AdjustEBOVGP-Dx

The AdjustEBOVGP-Dx project has been developing and testing a rapid point-of-care diagnostic to detect Ebola virus and to distinguish Ebola from a close relative, Marburg virus. The prototype was initially going to be tested in the Ebola outbreak region in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. However, as the outbreak was brought under control relatively quickly, the testing was carried out in South Africa using cultured virus from samples collected in Sierra Leone during the 2014-2015 outbreak. The consortium has engaged relevant authorities in local and international response to EVD in the region (INBR-DRC, MoH Uganda, FIND, WHO, etc.), and the team has established an ecosystem of GMP certified reagent suppliers and accredited RDT manufacturers (Astel Diagnostics ‘U' LTD & LifeAssays Incorp., SA) to rapidly scale up production and deployment of the RDTs. If proven clinically effective, it would be the first diagnostic able to identify infections with both Ebola and Marburg virus, another lethal viral infection with epidemic potential. As more outbreak occur, field validation of this diagnostic strategy continues, building on knowledge generated from the Emergency project.
Project Coordinator: Dr Misaki Wayengera, Makerere University, Uganda
Other Beneficiaries:
- National Institute for Communicable Diseases-NICD, South Africa
- Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences-SLU, Sweden
- University of Warsaw, Poland
- Agricultural University of Athens, Greece
- GeneCUST S.A.S, France